How HERITΛGE is using Generative AI to improve cultural heritage funding
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has taken the world by storm — transforming the way we write, design, and make decisions. But at HERITΛGE, we’re exploring how it can achieve something even more meaningful: help us understand, evaluate, and support community-led cultural heritage projects.
In 2023 HERITΛGE launched a call inviting and receiving hundreds of proposals from organizations, communities, and individuals in Africa to apply for small grants for Africa heritage projects — from traditional crafts and oral histories to sustainable tourism and cultural education. This was part of our HerMaP Africa initiative, supported by the Mellon Foundation.
The response was phenomenal. We received an unprecedented number of proposals from around the continent, over 1,700. A committee of experts was set up to examine them and decide which projects would be funded – no easy task!
To ensure that our funding decisions were fair, transparent, and data-driven, following the completion of the committee’s work, we joined forces with researchers from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and Institute of Computer Science, Foundation for Research and Technology – Hellas (FORTH) – also our partners in the EU-funded SHIFT project, and the Group on Language, Audio, and Music (GLAM), at Imperial College London. Together, we set out to answer a simple but powerful question:
Can open, ethical AI help us make smarter and more equitable funding decisions?
The researchers, including HERITΛGE director, Dr. Evangelos Kyriakidis,introduced a framework that developed a new framework to analyze large collections of project proposals in the cultural heritage field — using a mix of established methods and the latest artificial intelligence (AI).
Our goal was to understand what themes and priorities appeared most often in proposals, and what factors might influenced their success.
To do this, we combined traditional topic modeling tools (which find recurring themes in texts) with large language models (LLMs) — the same kind of advanced AI behind tools like ChatGPT.
First, the traditional models identified broad topics across more than 1,700 project proposals focused on protecting and promoting heritage in Africa. Then, newer AI models refined these themes, helping us define them more precisely and in ways that make sense for the heritage field.
We also looked at how language was used in the proposals — for example, how complex the writing was, what tone it used (positive or negative), and whether certain patterns in language might influence how proposals are received.
This approach helped uncover hidden insights about how funding is distributed and what kinds of projects tend to succeed. Ultimately, the aim is to support more transparent and equitable funding decisions and to help cultural heritage organizations better tailor their proposals for impact.
Putting Ethics and Privacy First
While many people are familiar with AI tools like ChatGPT, these are proprietary systems that store data on external servers. When dealing with sensitive information such as grant proposals, that’s a serious concern.
Instead of sending data to the cloud, we used an open-source AI model (LLaMA3) and ran it entirely on our own secure systems. This ensured that all proposal data remained private and compliant with our ethical standards.
Finding Meaning in 1,700 Proposals
Our analysis identified 25 meaningful categories reflecting heritage priorities and emerging trends in real work on the ground in Africa— from agricultural heritage to sustainable crafts and inclusive education.
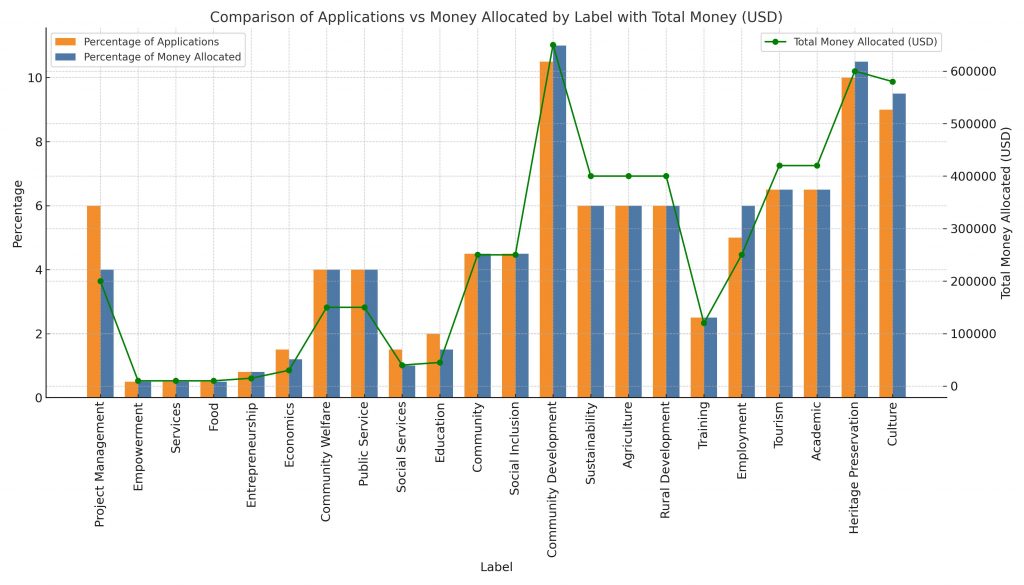 What we learnt was that Community Development, Heritage Preservation, and Culture emerged as the most common and well-funded themes. The figure below depicts how over $1 million of total allocations was apportioned among the 25 refined topics. Three leading categories—Community Development, Heritage Preservation, and Culture—each received close to $600,000. Meanwhile, areas like Social Services and Education fell below $50,000, indicating potential gaps in support.
What we learnt was that Community Development, Heritage Preservation, and Culture emerged as the most common and well-funded themes. The figure below depicts how over $1 million of total allocations was apportioned among the 25 refined topics. Three leading categories—Community Development, Heritage Preservation, and Culture—each received close to $600,000. Meanwhile, areas like Social Services and Education fell below $50,000, indicating potential gaps in support.
Interestingly, Tourism and Academic work secured comparatively large allocations despite a smaller share of total applications, highlighting a more targeted focus in these areas. Keep in mind here that applicants had to demonstrate that their project has a lasting impact, develops capacity, builds networks, strengthens local skills, and has a strong, measurable impact for the protection of heritage and the benefit of local people.
Some topics tended to appear together. Our analysis showed that strong overlaps emerged among Community Development, Culture, and Heritage Preservation, implying that community-driven initiatives often intersect with preserving local culture. Similarly, Sustainability, Conservation, and Agriculture frequently clustered, reflecting an expanding emphasis on environmentally responsible heritage initiatives. By contrast, topics like Training, Business, and Economics tended to appear in isolation—suggesting room for more integrated, cross-cutting proposals (e.g. heritage based social enterprises).
We also used sentiment analysis, readability measures, and inclusivity keywords to study the “linguistic fingerprint” of each proposal: we found that sentiment, readabilitty and inclusivity all mattered. Accepted proposals scored higher in positivity, suggesting that evaluators respond well to an upbeat, confident tone. Both successful and unsuccessful proposals were typically quite technical, indicating that complexity alone isn’t a deal-breaker. However, a moderate level of clarity—i.e., avoiding overly dense jargon—tended to correlate with better outcomes. Terms like “diversity” and “accessibility,” as well as a moderate usage of gendered pronouns, appeared more frequently in awarded projects. This underscores the value placed on inclusivity and social impact within cultural heritage funding.
In plain terms, AI confirmed that trojects using positive and inclusive language tended to perform better with evaluators, showing that tone and clarity influence evaluation outcomes. These insights can guide future applicants toward stronger, more effective proposals.
Why It Matters
By uncovering patterns in both what applicants propose and how they articulate their projects, we can provide clearer guidance for future calls and better ensure that funding reaches impactful cultural heritage initiatives.
This study shows that AI, when used ethically, can help cultural heritage professionals make funding processes more transparent, efficient, and fair. It’s not about replacing human judgment but enhancing it with better data and insights — ensuring that resources reach the initiatives with the greatest impact.
HERITΛGE and its partners will continue refining this approach as a new call for proposals for heritage projects in Mexico will soon be published, under our recently launched HerMaP Mexico initiative.
You can find the study and more information on the TUM website.

