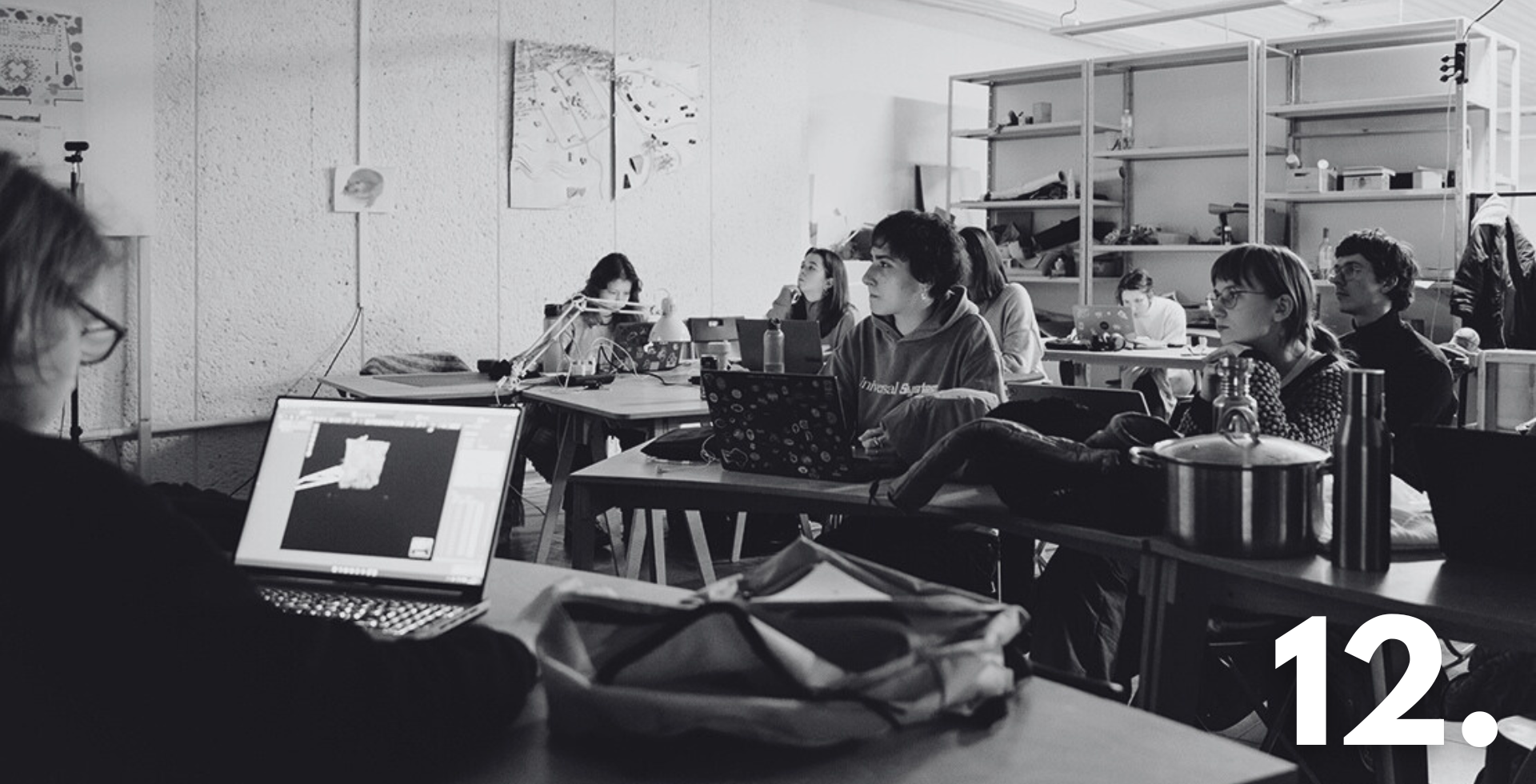
: HerMaP Mexico
New grants initiative for northern Mexico
 We are very happy to announce a brand new call for grants for heritage projects in Mexico. Our new call for proposals is aimed at organizations, groups, and individuals working with cultural heritage in northern Mexico, in the states of Baja California, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo Leon, Sonora and Tamaulipas. HERITΛGE will offer grants ranging from USD 10,000 to USD 50,000 per project.
We are very happy to announce a brand new call for grants for heritage projects in Mexico. Our new call for proposals is aimed at organizations, groups, and individuals working with cultural heritage in northern Mexico, in the states of Baja California, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo Leon, Sonora and Tamaulipas. HERITΛGE will offer grants ranging from USD 10,000 to USD 50,000 per project.
The grants are part of the HerMaP-Mexico, an initiative supported by the Mellon Foundation’s Humanities in Place program, to strengthen cultural heritage management and networks in northern Mexico. They will fund projects that focus on the protection of and/or promotion of local heritage for socio-economic development across the Mexico’s six northern border states.
All projects must clearly focus on the protection, safeguarding, strengthening, and/or promotion of local heritage, from approaches that recognize its cultural, social, and community value.
There are three main criteria for selecting proposals under this program:
- Sustainability- Priority will be given to projects that generate a lasting impact and whose positive effects extend beyond the support period.
- Capacity building and network strengthening – Projects that contribute to strengthening local capacities and establishing or consolidating links with similar organizations within heritage management networks will be encouraged.
- Concrete and Community Impact – Priority will be given to proposals that present clear, measurable, and verifiable results in terms of heritage protection and direct benefits for local communities. Each project must define specific indicators of the expected impact.
This call for proposals is the first phase of the selection process. Following an initial review, the shortlisted projects will be invited to submit an expanded and more detailed proposal. These complete proposals will be evaluated by the HerMaP Mexico program’s Support Committee.
The deadline for submitting proposals for this first phase is April 15, 2026. The final selection of supported projects will be announced no later than July 2026.
Contribute to a new mapping initiative in Northern Mexico
HERITΛGE has launched a new collaborative effort to map the cultural heritage sector across Mexico’s six northern border states — Baja California, Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas — and is inviting heritage professionals, community organizations, educational institutions, researchers, and cultural actors in the region to take part by completing a dedicated survey.
The mapping initiative forms part of HerMaP Mexico, a program funded by the Mellon Foundation that seeks to strengthen cultural heritage management across the northern border region of the country. Through HerMaP Mexico, HERITΛGE works collaboratively with local actors to support training processes, build professional and institutional networks, and assist community-led projects that promote sustainable cultural development.
By participating in the survey, contributors will help identify existing capacities, challenges, and opportunities in the heritage sector. The results will directly inform the design of context-sensitive training programs, technical support, and future program activities tailored to the realities of the region.
“At the heart of HerMaP Mexico is the belief that heritage is best managed when local knowledge, experience, and community voices are recognized and supported,” said HERITΛGE Director, Dr. Evangelos Kyriakidis. “This mapping process is a key step toward ensuring that future training and support respond to real needs on the ground.”
Cultural heritage encompasses far more than monuments or collections. It includes living traditions, local knowledge, historic places, cultural practices, and the people who sustain them. Effective heritage management helps ensure that these cultural resources are protected and shared in ways that benefit communities socially, culturally, and economically.
HERITΛGE invites all those working with cultural heritage in Mexico’s northern border states to contribute to this mapping effort by completing the survey.
Access the survey here: https://heritagemanagement.jotform.com/251043774849970
HERITΛGE 2025 Wrap-Up
In 2025, HERITΛGE continued to translate its mission of community-centred, inclusive, and sustainable heritage management into action across continents. From building local capacity across the world to advancing digital innovation and participatory practice in Europe and beyond, the year was defined by strong partnerships, expanded training, and tangible impact. HERITΛGE’s work in 2025 demonstrated how heritage can act as a driver of resilience, dialogue, and long-term social value, rooted in communities, connected globally, and oriented firmly toward the future.
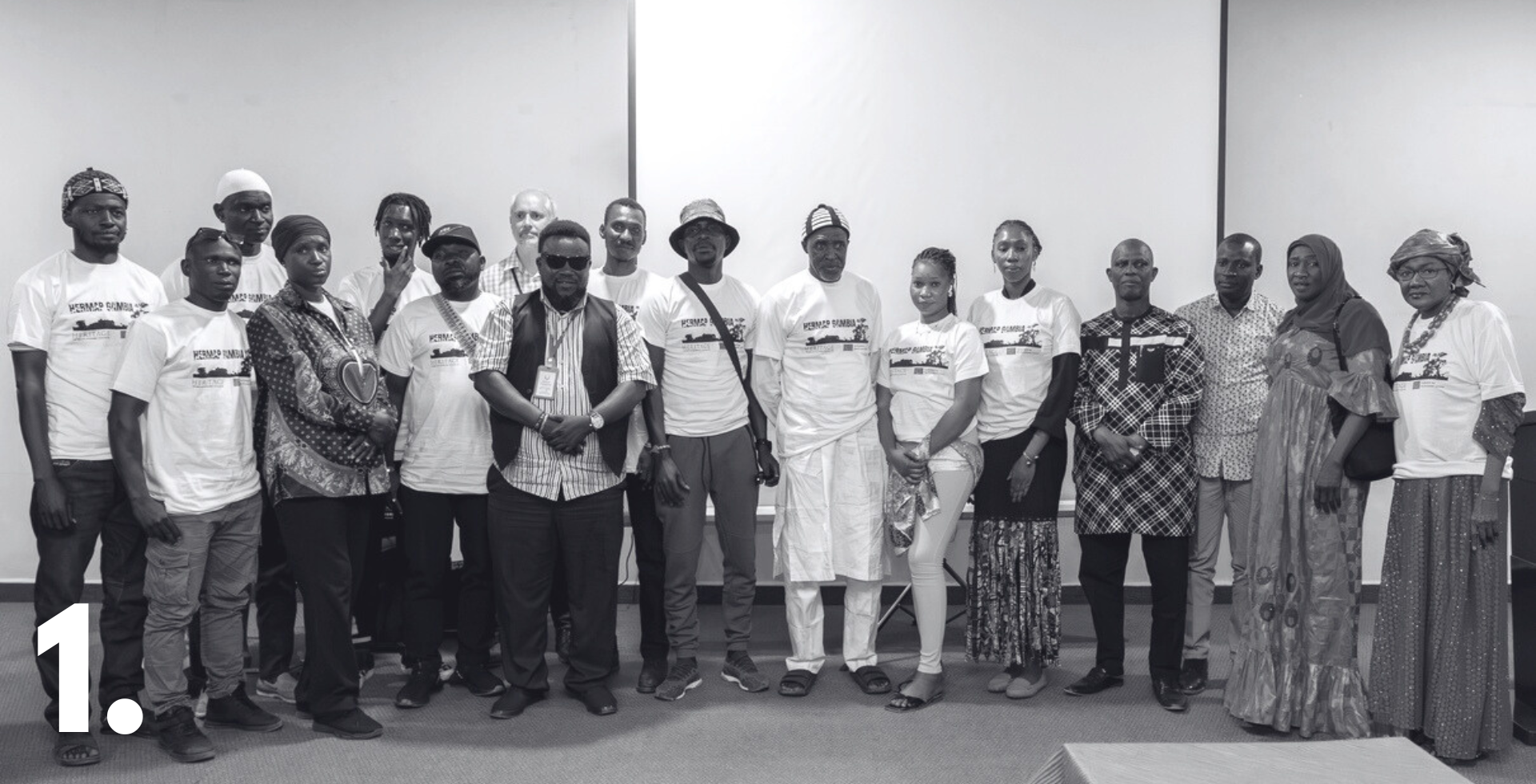
1.The HerMaP Gambia successful completion
In February, HERITΛGE marked the successful completion of HerMaP Gambia, an initiative co-funded by the EU, by celebrating a milestone in community-driven heritage management. A certificate ceremony and visual art exhibition was held as part of The Gambia’s 60th Independence Anniversary celebrations, bringing together EU representatives, parliamentarians, and the Chair of the National Assembly to honour the dedication of the programme’s trainees. One week later, the Minister of Tourism, Members of Parliament, EU representatives, and a broad range of stakeholders convened for a high-level stakeholder lunch focused on sustaining the transformative results of the project. Already, we are seeing HerMaP Gambia graduates applying their new skills across the country—strengthening local heritage initiatives, engaging communities, and even training others. The programme’s impact is now firmly rooted in the sector, creating momentum that will shape heritage management in The Gambia for years to come.
2. HerMaP Africa: Building Capacity and Partnerships Across Three Countries
In 2025, HERITΛGE deepened its impact across Ethiopia, Ghana, and Rwanda through targeted capacity building, strategic partnerships, and close engagement with local cultural ecosystems, as part of the HerMaP Africa initiative supported by the Mellon Foundation. In Ethiopia, HERITΛGE delivered seven workshops and trained 127 participants, with a strong emphasis on hands-on, in-person conservation training. Notably, conservation workshops in Harar focused on equipping the next generation of staff from the Culture and Tourism Bureau with practical skills to safeguard this unique living heritage site, reinforcing long-term, community-based preservation. Institutional collaboration was further strengthened through the signing of two Memoranda of Understanding with key Ethiopian organisations. In Ghana, HERITΛGE delivered four workshops and trained 80 participants, ensuring broad regional representation and inclusive access to capacity building beyond major urban centres. A national networking roundtable brought together stakeholders and project leaders to exchange experiences, align priorities, and address shared challenges in the heritage sector, alongside the signing of two strategic MoUs. In Rwanda, four workshops trained 78 participants, and three MoUs were signed with leading institutions, including a milestone partnership with the Ministry of Youth and Arts. HERITΛGE also contributed to the Ubumuntu Arts Festival through programme consultations and a participatory session with young creatives, strengthening connections between heritage, contemporary culture, and youth engagement. Across all three countries, a dedicated Train-the-Trainers programme equipped 19 heritage professionals to act as HERITΛGE ambassadors, significantly amplifying local capacity and long-term impact.
3. Small Grants for African Heritage
 The regranting phase of HerMaP Africa reached its conclusion, marking one of the most ambitious and impactful heritage-support programmes on the continent. Since 2023, HERITΛGE has received more than 2,500 applications from across Africa and funded over 74 small heritage projects, each led by local actors working to safeguard, reinterpret, and activate their cultural heritage. This regranting initiative was made possible with the generous support of the Mellon Foundation. Throughout the year, grantees participated in six regional convenings, creating spaces to exchange experiences, strengthen their skills, and learn from peers—building a growing network of practitioners committed to community-centred heritage work. Several more convenings are planned for 2026 to continue nurturing this collaborative ecosystem. The results have been remarkable: from revitalised cultural practices to restored and more resilient cultural sites, to new opportunities for local development, these projects are already transforming lives. We are proud to showcase this work through dedicated social media features and a new publication that brings together the stories, challenges, and achievements of the HerMaP Africa grantees.
The regranting phase of HerMaP Africa reached its conclusion, marking one of the most ambitious and impactful heritage-support programmes on the continent. Since 2023, HERITΛGE has received more than 2,500 applications from across Africa and funded over 74 small heritage projects, each led by local actors working to safeguard, reinterpret, and activate their cultural heritage. This regranting initiative was made possible with the generous support of the Mellon Foundation. Throughout the year, grantees participated in six regional convenings, creating spaces to exchange experiences, strengthen their skills, and learn from peers—building a growing network of practitioners committed to community-centred heritage work. Several more convenings are planned for 2026 to continue nurturing this collaborative ecosystem. The results have been remarkable: from revitalised cultural practices to restored and more resilient cultural sites, to new opportunities for local development, these projects are already transforming lives. We are proud to showcase this work through dedicated social media features and a new publication that brings together the stories, challenges, and achievements of the HerMaP Africa grantees.
4. HerMaP Mexico: Launching a New Border Region Initiative
This year also marked the launch of HerMaP Mexico, a major new initiative that expands HERITΛGE’s work into North America and supports cultural heritage actors across Mexico’s northern border states. Funded by the Mellon Foundation’s Humanities in Place programme, the project brings a comprehensive, community-focused approach to heritage management through mapping, training, networking, and small grants. In 2025 we established the foundations of the programme: building local partnerships, initiating the mapping of heritage professionals and institutions across six states, and preparing the first round of capacity-building workshops to be delivered in both Spanish and English. HerMaP Mexico responds to the region’s unique cultural landscape—shaped by Indigenous, mestizo, migrant, and Chicano communities—and aims to strengthen local skills while creating new opportunities for collaboration and sustainable development. As the project moves forward, it will support locally led initiatives and grow into a long-term platform that connects heritage practitioners across the border region with global networks and resources.
5. Professional Training and Executive Leadership Education Programmes
HERITΛGE continued to strengthen its leadership in professional training by expanding its Executive Leadership Education programmes and reinforcing its global learning community. A key milestone was the introduction of Community Tourism and Development into the curriculum, responding to the growing need for heritage managers to understand how cultural resources can generate sustainable economic benefits while reinforcing social cohesion, identity, and community resilience. This year also saw the first alumni conference of the Engaging Communities in Cultural Heritage Summer School, bringing together former participants from around the world to share research, field experiences, and community-based practices. Alongside this, HERITΛGE successfully delivered its Conservation Series Training Programmes for the second time, expanding the offer to include First Aid for Finds and Preventive Conservation, and equipping participants with practical skills applicable across diverse heritage contexts. The Training of Trainers (ToT) programme continued to grow, building a global cohort of HERITΛGE Ambassadors—heritage professionals trained to deliver high-quality, cross-cultural capacity building within their own communities. Together, these initiatives reflect HERITΛGE’s ongoing commitment to community-centred heritage management, interdisciplinary collaboration, and the empowerment of professionals working at the intersection of culture, development, and sustainability, supported by a vibrant international network united by shared values and collective impact.
6. Advancing Audience-Centred Heritage Practice through AHEAD
In 2025, HERITΛGE advanced its work on audience-centred heritage practice through AHEAD (Accessible Heritage Experience for Audience Development), a project co-funded by Creative Europe and dedicated to strengthening participation, co-creation, and sustainability across the cultural heritage sector. At the Archaeological Museum of Messara, the project’s Greek hub, HERITΛGE hosted a series of co-creation labs in early 2025, followed by a study visit for AHEAD project partners in May, creating space for peer learning and in-depth exchange around participatory heritage approaches. In July, the 3rd AHEAD Networking Event brought together practitioners and researchers, and featured the presentation of the Living Heritage Network in Greece by Theodosia Maroutsi, highlighting how community-led approaches can be embedded in national heritage ecosystems. In September, HERITΛGE organised a dedicated Multiplier event in Athens to share the results of AHEAD with heritage managers, researchers, and cultural professionals. The project culminated in October with the presentation of AHEAD and its outcomes in Brussels and, for the Greek hub, a public event at the Archaeological Museum of Messara, where Elektra Angelopoulou, the project’s artist-in-residence, presented a site-specific artwork co-created with the local community. Alongside these events, AHEAD produced a dedicated magazine and learning resources that document the project’s insights and offer practical tools for fostering co-creation, inclusion, and long-term sustainability in cultural heritage practice.
7. SHIFT: Inclusive Digital Innovation for the Future of Cultural Heritage
HERITΛGE and its SHIFT consortium partners concluded this ambitious Horizon Europe project aimed at making cultural heritage more accessible, inclusive, and engaging through advanced technologies. Over its lifetime, SHIFT delivered a suite of innovative tools—including an Image-to-Video generator, affective speech synthesis, haptics interfaces, and a platform designed to support inclusive digital storytelling—alongside a pioneering Extended Reality (XR) Accessibility Framework. These results were tested and refined through four pilot events in Germany, Hungary, Romania, and Serbia, ensuring that the tools responded to real needs within museums, libraries, and cultural organisations. The project’s achievements were showcased at major gatherings such as the Digital Heritage World Congress and Expo in Siena, highlighting SHIFT’s contribution to the future of digital cultural heritage. As part of our commitment to long-term impact, HERITΛGE developed a set of training modules to equip cultural heritage professionals with the skills they need to adopt and apply these new technologies in their own contexts.
8. Strengthening a National Platform for Living Heritage
HERITΛGE strengthened its commitment to living heritage in Greece as a founding member of the country’s Living Heritage Network, with our Greek Programmes Manager, Theodosia Maroutsi, serving for the third year on its coordinating committee. In this role, HERITΛGE actively contributed to the Network’s 2nd National Meeting, held in Athens on 21–23 February, a major highlight of the year, where Theodosia welcomed participants and drove the dialogue during the “Living Heritage Network: Formation and Perspectives” roundtable “ reflecting on the Network’s development and future direction. HERITΛGE also delivered one of the leading side events of the 2nd National Meeting, a hands-on workshop, for 30 participants, titled “Working on the Narrative Interpretation of Living Cultural Heritage,” supporting practitioners in exploring narrative approaches to interpreting living heritage. Our impact extended well beyond the 2nd National Meeting’s floor. HERITΛGE was instrumental in drafting the Network’s Mapping Questionnaire, which was also launched in autumn of 2025. This Mapping is a crucial initiative designed to identify the essential needs of the living heritage ecosystem. The Network’s work was further amplified through HERITΛGE’s involvement in European projects: it was featured in AHEAD, where Theodosia participated in the 3rd Online Networking Event and was interviewed for the project’s magazine—freely available in English, Greek, Italian, and Spanish—and in EMPATHS, where the Network informed stakeholder mapping, cross-sector interviews, and co-design findings. Together, these activities positioned the Living Heritage Network as a key grassroots platform for participatory, community-led heritage practice in Greece and beyond.
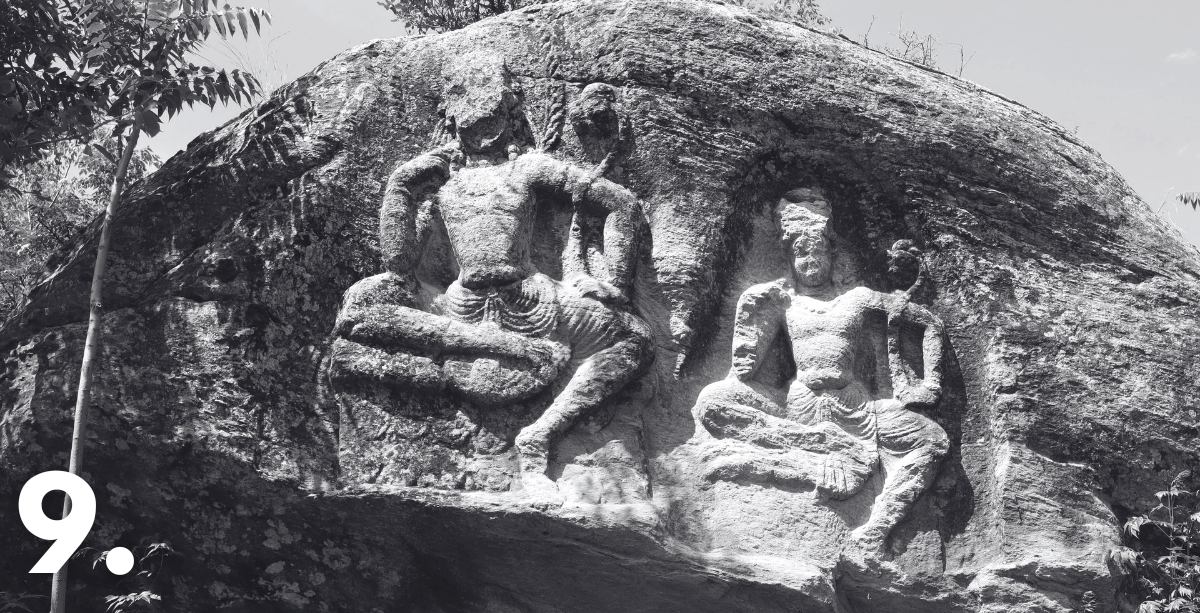
9. Safeguarding Pakistan’s Most Significant and Vulnerable Cultural Landscapes
HERITΛGE and our partners completed the first phase of the project Preservation of Buddhist Rock Reliefs in the Swat Valley, safeguarding one of Pakistan’s most significant and vulnerable cultural landscapes. The initiative documented and conserved Buddhist rock carvings dating from the 8th to the 10th centuries, while also recording oral histories, legends, and traditional arts and crafts that link Pashtun culture with the Valley’s Buddhist past. Using advanced digital techniques, 78 rock reliefs were documented and made accessible through a public website featuring interactive maps and 3D models, and first aid conservation was carried out on 39 of the most at-risk sites. Capacity building was central to the project, with local participants trained in digital documentation and climate change adaptation. This first phase concluded with a public event at the Swat Museum and was presented internationally, including at the Lahore Museum, the Venice Biennale, and COP30, where it was cited as a strong example of heritage resilience in the face of climate change. Funded by the British Council’s Cultural Protection Fund and implemented with local and international partners, the project demonstrates how conservation, community engagement, and digital innovation can work together to protect heritage for future generations.
10. EMPATHS: Advancing Participatory Heritage Interpretation Across Europe
In 2025, HERITΛGE deepened its engagement in the Erasmus+–funded EMPATHS project, which aims to equip heritage professionals with the skills needed for participatory, community-driven heritage interpretation. Early in the year, the project contributed to international dialogue through a LDnet webinar on empowering local communities for smart and sustainable cultural heritage, while in May it published the EMPATHS Baseline Report, offering a comprehensive overview of current practices, challenges, and opportunities in participatory heritage interpretation across Europe and beyond. EMPATHS was further showcased at the European Association of Archaeologists (EAA) Congress in Belgrade, through the session “Voices of the Past, Hands of the Present: Collaborative Pathways in Archaeology and Heritage Interpretation.” In parallel, HERITΛGE led two online co-design sessions in Greece with heritage professionals from Alexandroupoli and Rizía, marking the project’s first structured dialogue between technical partners and piloting organisations and directly informing the design of the forthcoming training programme. Over the summer, EMPATHS published four key deliverables, including stakeholder mapping, cross-sector interviews, and co-design findings, all reinforcing the demand for skills in facilitation, storytelling, and emotionally resonant communication. The year culminated with the project’s second Transnational Project Meeting in Athens, where partners advanced work on the EMPATHS methodological compendium and training framework, the presentation of the project during a Global Alliance for Heritage Interpretation Webinar, and, importantly, with the publication of the EMPATHS Manifesto—a collective call to move beyond top-down interpretation and embrace heritage as a shared, democratic, and future-oriented process shaped with communities.
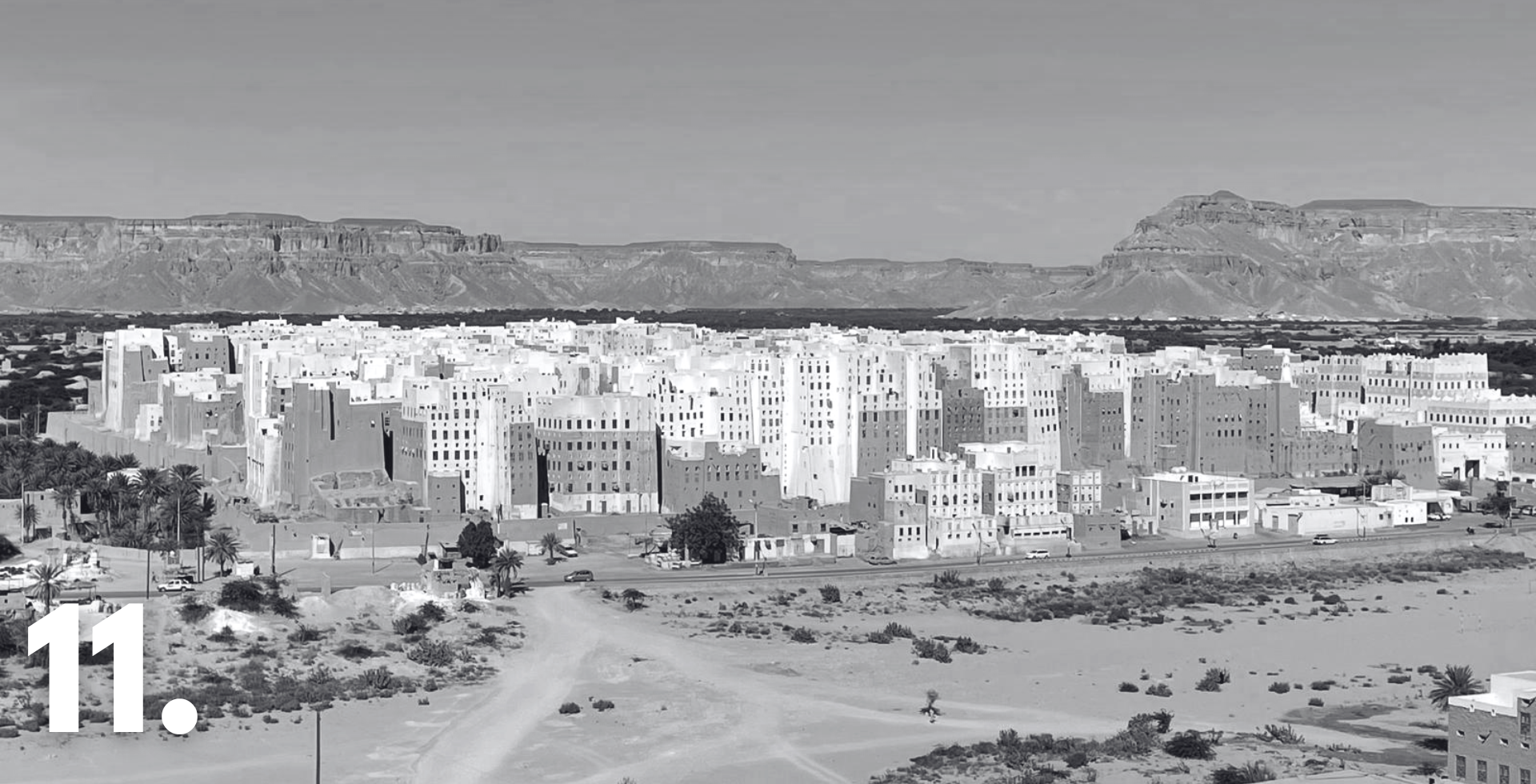
11. Community-Led Preservation of Earthen Architecture in Shibam, Yemen
In Yemen, HERITΛGE advanced a major effort to safeguard the cultural heritage of Shibam through the ALIPH-funded project Preserving the Unique Earthen Architecture of Shibam. In early 2025, museum experts Shatha Safi and Khulod Najjar travelled to the UNESCO World Heritage city to guide the community-led planning of a new museum that will bring together collections currently scattered across Shibam and create dedicated spaces for traditional arts, crafts, and digital learning. Their visit marked a pivotal moment in the project, with consultations held with local authorities, heritage institutions, and women from the community to ensure the museum reflects the lived experiences, history, and aspirations of Shibam’s residents. Alongside this vision-setting, HERITΛGE is training local professionals on-site, with four trainees already working with our team on the documentation of the South Palace—future home of the museum. Complemented by architectural assessments and a climate action study, the project is laying the groundwork for a resilient cultural hub that will support preservation and community engagement for years to come.
12. Safeguarding Architectural Heritage in Times of War in Ukraine
In Ukraine, HERITΛGE advanced critical work to protect architectural heritage threatened by war through the project Architectural Heritage Preservation in Times of War: The Ukrainian Model, delivered with the Kharkiv School of Architecture and 3D documentation specialists Skeiron. Launched in September 2024, the programme trained 30 students and 10 educators from across the country in cutting-edge documentation and conservation techniques—from photogrammetry and 3D laser scanning to international heritage standards—while providing hands-on field internships in Western Ukraine. Together, they created high-resolution digital records of 15 at-risk sites, safeguarding knowledge even as physical structures remain vulnerable. Through educator training and a series of public webinars, the project also planted the seeds for a new nationwide curriculum in architectural heritage preservation. Its impact extends far beyond a single academic year: it has built a cohort of young architects and teachers equipped with the skills, networks, and resolve to protect Ukraine’s cultural memory during conflict and beyond. Their work stands as a reminder that preserving heritage is not only an act of conservation, but an act of resilience and recovery.
13. New Projects for the Digital Transformation of Cultural Heritage
 In 2025, HERITΛGE became a consortium partner in two new projects funded under the EU’s Horizon Europe programme, both contributing to the ECHOES initiative and the development of the European Collaborative Cloud for Cultural Heritage (ECCCH). ECHOES aims to establish a shared digital infrastructure that brings together currently fragmented cultural heritage communities, offering access to data, advanced digital tools, scientific resources, and training materials developed collaboratively by heritage professionals and researchers. HERITΛGE participates in MusicSphere, a project dedicated to preserving and interpreting traditional musical organs—such as pipe organs and their ancient Greek counterpart, the hydraulis—through high-fidelity digital replicas, acoustic modelling, and immersive virtual and augmented reality experiences that capture both their physical structure and sonic interaction with architectural spaces. HERITΛGE is also a partner in EXCALIBUR, which focuses on burial sites, excavation contexts, artefacts, and human remains, developing human-centred, affordable digital twin technologies to support research, conservation, restoration, and museum interpretation. Together, these projects contribute to the long-term preservation, study, and public understanding of complex heritage assets, while ensuring that open, interoperable, and practitioner-driven tools are shared through the ECCCH platform for broad professional and societal impact.
In 2025, HERITΛGE became a consortium partner in two new projects funded under the EU’s Horizon Europe programme, both contributing to the ECHOES initiative and the development of the European Collaborative Cloud for Cultural Heritage (ECCCH). ECHOES aims to establish a shared digital infrastructure that brings together currently fragmented cultural heritage communities, offering access to data, advanced digital tools, scientific resources, and training materials developed collaboratively by heritage professionals and researchers. HERITΛGE participates in MusicSphere, a project dedicated to preserving and interpreting traditional musical organs—such as pipe organs and their ancient Greek counterpart, the hydraulis—through high-fidelity digital replicas, acoustic modelling, and immersive virtual and augmented reality experiences that capture both their physical structure and sonic interaction with architectural spaces. HERITΛGE is also a partner in EXCALIBUR, which focuses on burial sites, excavation contexts, artefacts, and human remains, developing human-centred, affordable digital twin technologies to support research, conservation, restoration, and museum interpretation. Together, these projects contribute to the long-term preservation, study, and public understanding of complex heritage assets, while ensuring that open, interoperable, and practitioner-driven tools are shared through the ECCCH platform for broad professional and societal impact.
How HERITΛGE is using Generative AI to improve cultural heritage funding
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has taken the world by storm — transforming the way we write, design, and make decisions. But at HERITΛGE, we’re exploring how it can achieve something even more meaningful: help us understand, evaluate, and support community-led cultural heritage projects.
In 2023 HERITΛGE launched a call inviting and receiving hundreds of proposals from organizations, communities, and individuals in Africa to apply for small grants for Africa heritage projects — from traditional crafts and oral histories to sustainable tourism and cultural education. This was part of our HerMaP Africa initiative, supported by the Mellon Foundation.
The response was phenomenal. We received an unprecedented number of proposals from around the continent, over 1,700. A committee of experts was set up to examine them and decide which projects would be funded – no easy task!
To ensure that our funding decisions were fair, transparent, and data-driven, following the completion of the committee’s work, we joined forces with researchers from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and Institute of Computer Science, Foundation for Research and Technology – Hellas (FORTH) – also our partners in the EU-funded SHIFT project, and the Group on Language, Audio, and Music (GLAM), at Imperial College London. Together, we set out to answer a simple but powerful question:
Can open, ethical AI help us make smarter and more equitable funding decisions?
The researchers, including HERITΛGE director, Dr. Evangelos Kyriakidis,introduced a framework that developed a new framework to analyze large collections of project proposals in the cultural heritage field — using a mix of established methods and the latest artificial intelligence (AI).
Our goal was to understand what themes and priorities appeared most often in proposals, and what factors might influenced their success.
To do this, we combined traditional topic modeling tools (which find recurring themes in texts) with large language models (LLMs) — the same kind of advanced AI behind tools like ChatGPT.
First, the traditional models identified broad topics across more than 1,700 project proposals focused on protecting and promoting heritage in Africa. Then, newer AI models refined these themes, helping us define them more precisely and in ways that make sense for the heritage field.
We also looked at how language was used in the proposals — for example, how complex the writing was, what tone it used (positive or negative), and whether certain patterns in language might influence how proposals are received.
This approach helped uncover hidden insights about how funding is distributed and what kinds of projects tend to succeed. Ultimately, the aim is to support more transparent and equitable funding decisions and to help cultural heritage organizations better tailor their proposals for impact.
Putting Ethics and Privacy First
While many people are familiar with AI tools like ChatGPT, these are proprietary systems that store data on external servers. When dealing with sensitive information such as grant proposals, that’s a serious concern.
Instead of sending data to the cloud, we used an open-source AI model (LLaMA3) and ran it entirely on our own secure systems. This ensured that all proposal data remained private and compliant with our ethical standards.
Finding Meaning in 1,700 Proposals
Our analysis identified 25 meaningful categories reflecting heritage priorities and emerging trends in real work on the ground in Africa— from agricultural heritage to sustainable crafts and inclusive education.
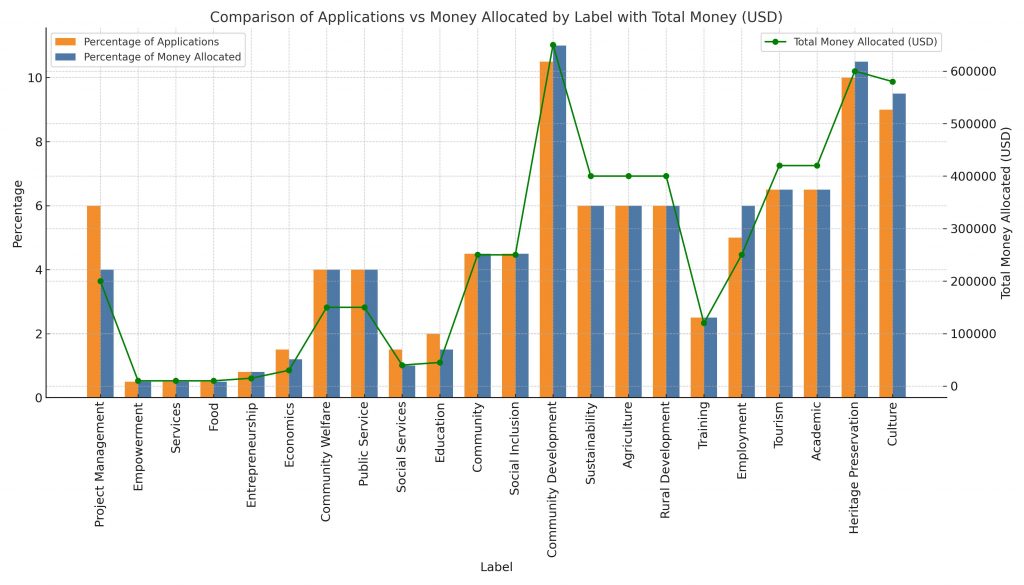 What we learnt was that Community Development, Heritage Preservation, and Culture emerged as the most common and well-funded themes. The figure below depicts how over $1 million of total allocations was apportioned among the 25 refined topics. Three leading categories—Community Development, Heritage Preservation, and Culture—each received close to $600,000. Meanwhile, areas like Social Services and Education fell below $50,000, indicating potential gaps in support.
What we learnt was that Community Development, Heritage Preservation, and Culture emerged as the most common and well-funded themes. The figure below depicts how over $1 million of total allocations was apportioned among the 25 refined topics. Three leading categories—Community Development, Heritage Preservation, and Culture—each received close to $600,000. Meanwhile, areas like Social Services and Education fell below $50,000, indicating potential gaps in support.
Interestingly, Tourism and Academic work secured comparatively large allocations despite a smaller share of total applications, highlighting a more targeted focus in these areas. Keep in mind here that applicants had to demonstrate that their project has a lasting impact, develops capacity, builds networks, strengthens local skills, and has a strong, measurable impact for the protection of heritage and the benefit of local people.
Some topics tended to appear together. Our analysis showed that strong overlaps emerged among Community Development, Culture, and Heritage Preservation, implying that community-driven initiatives often intersect with preserving local culture. Similarly, Sustainability, Conservation, and Agriculture frequently clustered, reflecting an expanding emphasis on environmentally responsible heritage initiatives. By contrast, topics like Training, Business, and Economics tended to appear in isolation—suggesting room for more integrated, cross-cutting proposals (e.g. heritage based social enterprises).
We also used sentiment analysis, readability measures, and inclusivity keywords to study the “linguistic fingerprint” of each proposal: we found that sentiment, readabilitty and inclusivity all mattered. Accepted proposals scored higher in positivity, suggesting that evaluators respond well to an upbeat, confident tone. Both successful and unsuccessful proposals were typically quite technical, indicating that complexity alone isn’t a deal-breaker. However, a moderate level of clarity—i.e., avoiding overly dense jargon—tended to correlate with better outcomes. Terms like “diversity” and “accessibility,” as well as a moderate usage of gendered pronouns, appeared more frequently in awarded projects. This underscores the value placed on inclusivity and social impact within cultural heritage funding.
In plain terms, AI confirmed that trojects using positive and inclusive language tended to perform better with evaluators, showing that tone and clarity influence evaluation outcomes. These insights can guide future applicants toward stronger, more effective proposals.
Why It Matters
By uncovering patterns in both what applicants propose and how they articulate their projects, we can provide clearer guidance for future calls and better ensure that funding reaches impactful cultural heritage initiatives.
This study shows that AI, when used ethically, can help cultural heritage professionals make funding processes more transparent, efficient, and fair. It’s not about replacing human judgment but enhancing it with better data and insights — ensuring that resources reach the initiatives with the greatest impact.
HERITΛGE and its partners will continue refining this approach as a new call for proposals for heritage projects in Mexico will soon be published, under our recently launched HerMaP Mexico initiative.
You can find the study and more information on the TUM website.
HERITΛGE launches HerMaP Mexico with Mellon Foundation Grant
Building on the success of HERITΛGE’s international programs, this new project represents a major milestone in the organization’s growing engagement in North America. It will bring together heritage professionals, community organizations, and cultural leaders from across the region to map heritage ecosystems, build capacity, and support community-led projects.
“We see HerMaP Mexico as a transformative initiative — both for the organization and for heritage professionals across Mexico’s border states,” said HERITΛGE’s Denise Navarro Becerra, HerMaP Mexico Project Manager. “With the Mellon Foundation’s generous support, we aim to connect and empower those heritage managers and stewards in one of the world’s most dynamic cultural regions.”
A Four-Pillar Approach to Strengthening Heritage
HerMaP Mexico’s activities are structured around four key pillars:
- Mapping: Identifying actors, capacities, infrastructure, and gaps in heritage management across the six states.
- Capacity Building: Delivering targeted heritage management training programs adapted to and inspired by the local contexts through in-person and online sessions.
- Networking: Organizing regional networking events to connect local, national, and international actors in heritage management.
- Re-granting: Distributing small grants to community-focused heritage projects.
These activities will engage a wide range of stakeholders and topics in cultural heritage management, highlighting the richness and diversity of the border region’s cultural heritage. The program will run until September 2027, combining in-person activities with digital learning resources available through HERITΛGE’s Training Platform.