Tag Archives: SHIFT
HERITΛGE Highlights 2024
Training
HERITΛGE celebrated a record-breaking milestone in 2024, training over 1,000 heritage caretakers in a single year. Participants engaged in a wide range of programs, including three-day workshops conducted online and in person, two annual summer schools focusing on digital tools and community engagement, and specialized training tailored to specific regions, topics and organizations. These included programs on Street Art in The Gambia (which also produced a new mural for the country’s National Centre for the Arts and Culture), Heritage interpretation in Rwanda, Project Management for US Heritage Managers, and an introduction to Fundraising and Project Management in Iraq.
Heritage Threatened by Conflict, Natural Disasters, and Climate Change
HERITΛGE continued its mission to protect heritage at risk worldwide, strengthening existing partnerships and forging new ones. In Ukraine, the Digital Museum project that was funded by the Creative Europe’s Culture Helps initiative, trained museum professionals to use digital tools, ensuring operational continuity and community access during wartime. Simultaneously, the two-year Architecture in Times of War: The Ukrainian Model initiative – delivered in cooperation with the Kharkiv School of Architecture and Skeiron and the support of the US Embassy in Kyiv – is equipping students and educators with digital skills to document, preserve, and restore architectural heritage.
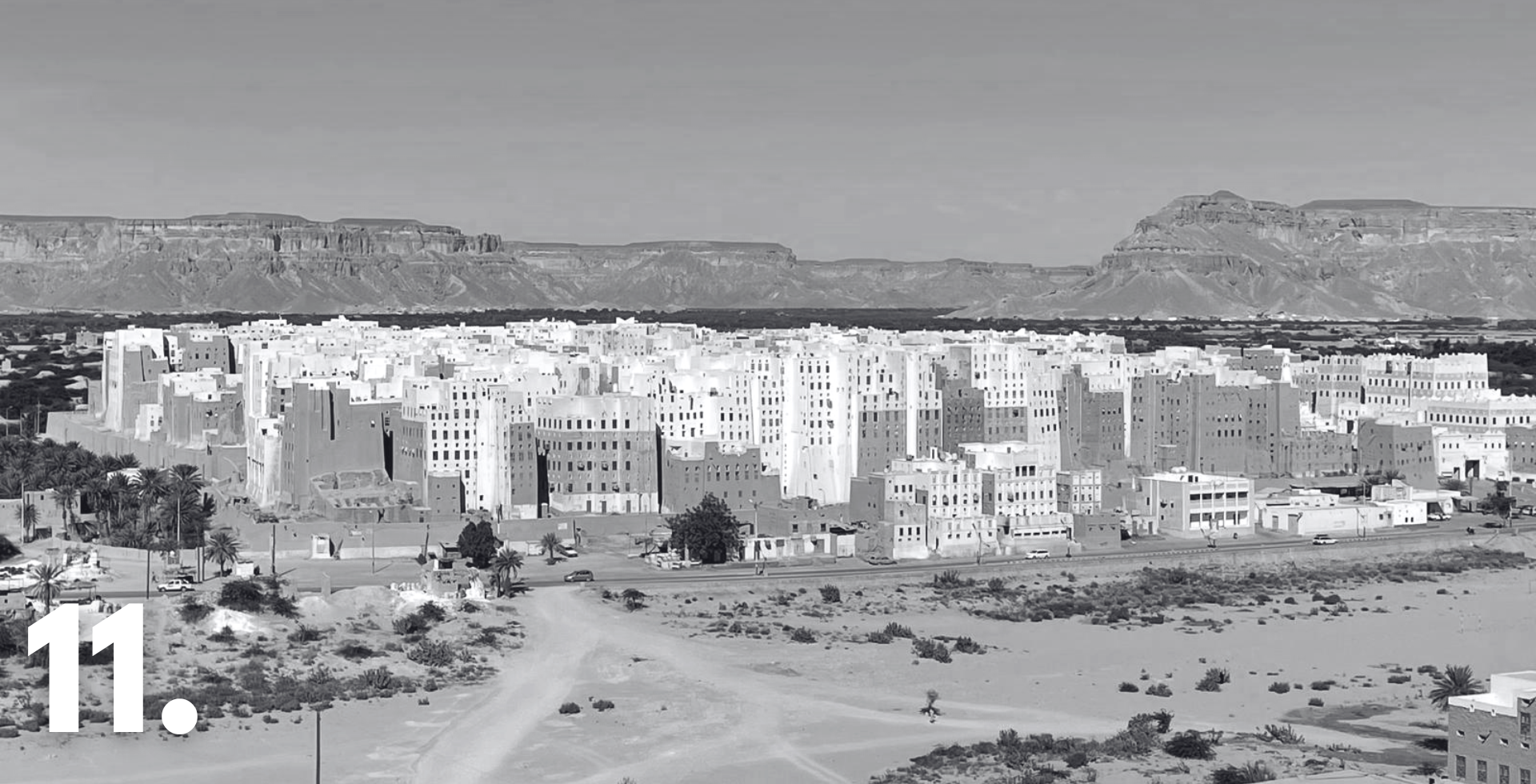
In Türkiye, HERITΛGE published comprehensive reports documenting historic sites affected by the February 2023 Türkiye-Syria earthquakes. These reports include protection recommendations and advocate for enhanced cultural heritage recovery in affected provinces. Meanwhile, in Pakistan, a new project launched to safeguard the early Buddhist heritage of the Swat Valley, an area under threat from conflict, climate change, and rapid development. In Yemen, efforts continued to preserve the unique earthen architecture of Shibam, a UNESCO World Heritage Site struggling under the weight of a decade-long civil war.
HERITΛGE in Africa
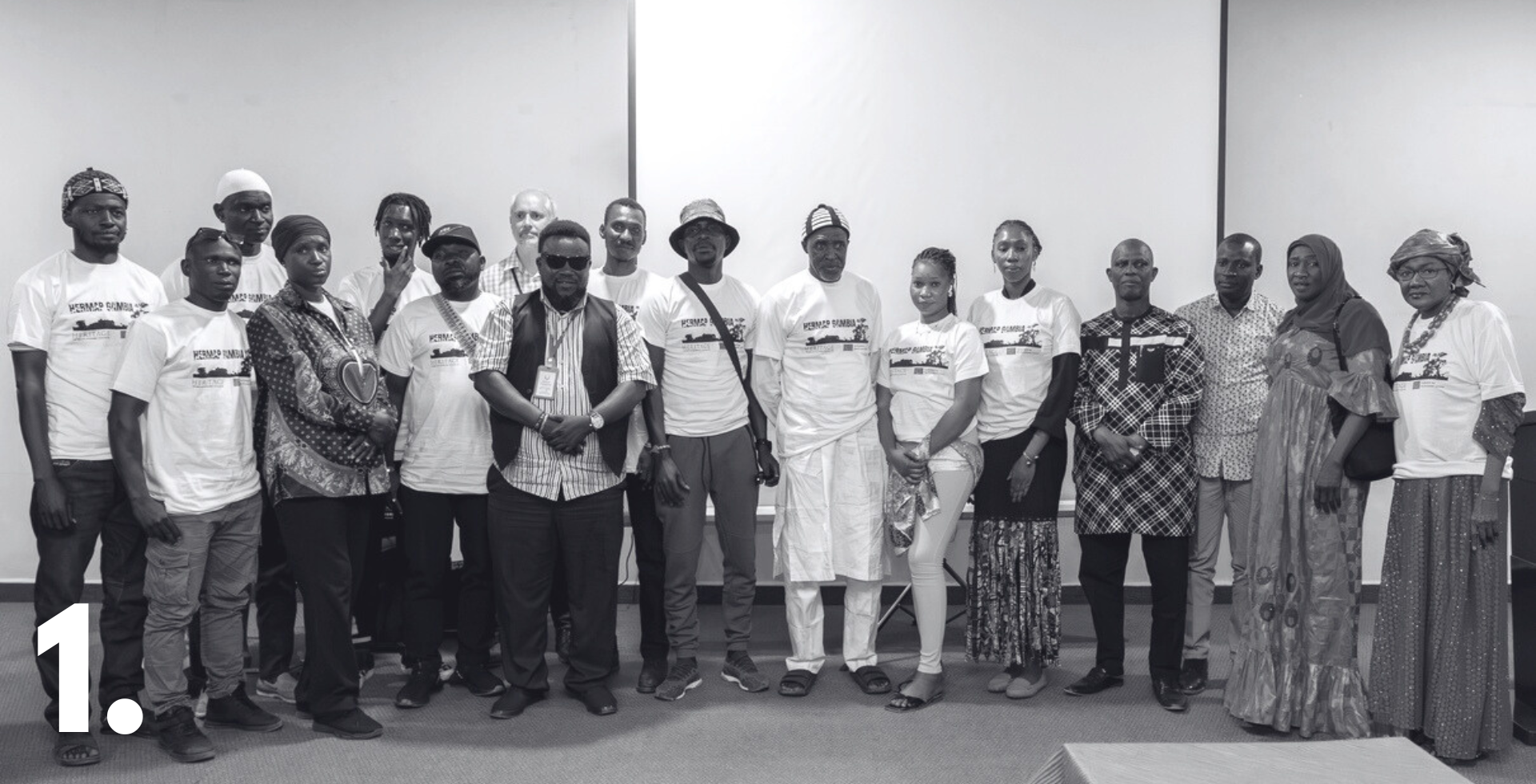
The HerMaP Africa initiative, generously supported by the Mellon Foundation, has delivered significant impact. Over 75 small heritage projects received funding, alongside the awarding of several fellowships and the training of more than 370 heritage managers in Ethiopia, Ghana, and Rwanda. New partnerships were also established to further these efforts. In The Gambia, HERITΛGE’s ongoing HerMaP Gambia initiative, co-funded by the European Union, provided training to enhance the country’s culture and tourism sectors. The program also facilitated a parliamentary delegation study tour in Greece and partnered with the NCAC to launch the country’s Intangible Cultural Heritage Register, a project supported by UNESCO.
Giving Heritage Managers New Tools
HERITΛGE made strides in empowering heritage managers with innovative tools and practices. The EU-funded SHIFT project advanced its work to make heritage more accessible and inclusive, with a consortium meeting and project presentation held in Athens. The AHEAD initiative, co-funded by the European Union’s Creative Europe program, introduced seminars (now available online) and launched a community-based artistic project in Crete, with similar activities planned for Italy and Spain. HERITΛGE also announced the launch of EMPATHS, a project designed to promote participatory heritage interpretation through new tools and training resources.
Creating Networks, Connecting Professionals
Collaboration and community-building remained central to HERITΛGE’s mission in 2024. The organization continued developing Greece’s Living Heritage Network, supported by the Ministry of Culture, with HERITΛGE actively contributing to its digital and physical infrastructure, member recruitment, and communications. Additionally, the newly established AHEAD Network brings together heritage managers and community members who share a vision of audience engagement and participation.
Knowledge Sharing
HERITΛGE emphasized the importance of knowledge-sharing through active participation in global events and publications. Director Dr. Evangelos Kyriakidis delivered a keynote at the Choc Des Legendes Conference in Ghana, held under the auspices of the country’s First Lady. The organization also sponsored PastForward 2024, the annual conference of the US National Trust for Historic Preservation. Other highlights included workshops and presentations at the 30th Annual Meeting of the European Association of Archaeologists and the ReImagining Public Collections conference in Hungary.
HERITΛGE contributed to a Horizon Europe-funded policy brief on digital cultural heritage and shared expertise through webinars, seminars, and public lectures. Notable online resources include audience development webinars from the AHEAD initiative and webinars on architectural preservation in Ukraine.
1st Global Staff Summit
Reflecting the growth in HERITΛGE’s activities and team, the organization hosted its inaugural Global Staff Summit in September. This online event brought together staff working in Africa, Asia, Europe and the Americas , marking the beginning of an annual tradition to foster collaboration and alignment across our expanding network.
New SHIFT publications
HERITΛGE is proud to be part of the SHIFT project, collaborating with 12 partners, including heritage organizations, universities, research centers, and private businesses. Together, we aim to make cultural heritage more accessible, inclusive, and engaging by leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and haptics.
This year, the project has delivered two important publications, both available for free download:
Inclusion in Museums: A Collection of Best Practices
Produced by the Balkan Museum Network (BMN), this e-book showcases best practices for fostering inclusion in museums across the Balkans. The publication features insights from heritage experts on implementing inclusive strategies, highlighting successes, identifying challenges, and outlining steps for future progress. An audiobook version will be available soon.
Promoting Inclusive Innovation in Digital Technologies for Heritage Preservation
SHIFT, along with four sister projects funded under Horizon Europe’s 2021 call for proposals (Cluster 2: Culture, Creativity & Inclusive Society), has released a collaborative policy brief. This document provides actionable recommendations for policymakers to address expertise gaps, enhance digital education, and promote inclusion within the cultural heritage sector. Download the policy brief to learn more.
SHIFT is funded under the European Union’s Horizon Europe program, Cluster 2: “Culture, Creativity & Inclusive Society,” which focuses on innovative research in European cultural heritage and the cultural and creative industries.
Stay tuned for more SHIFT updates and developments in 2025!
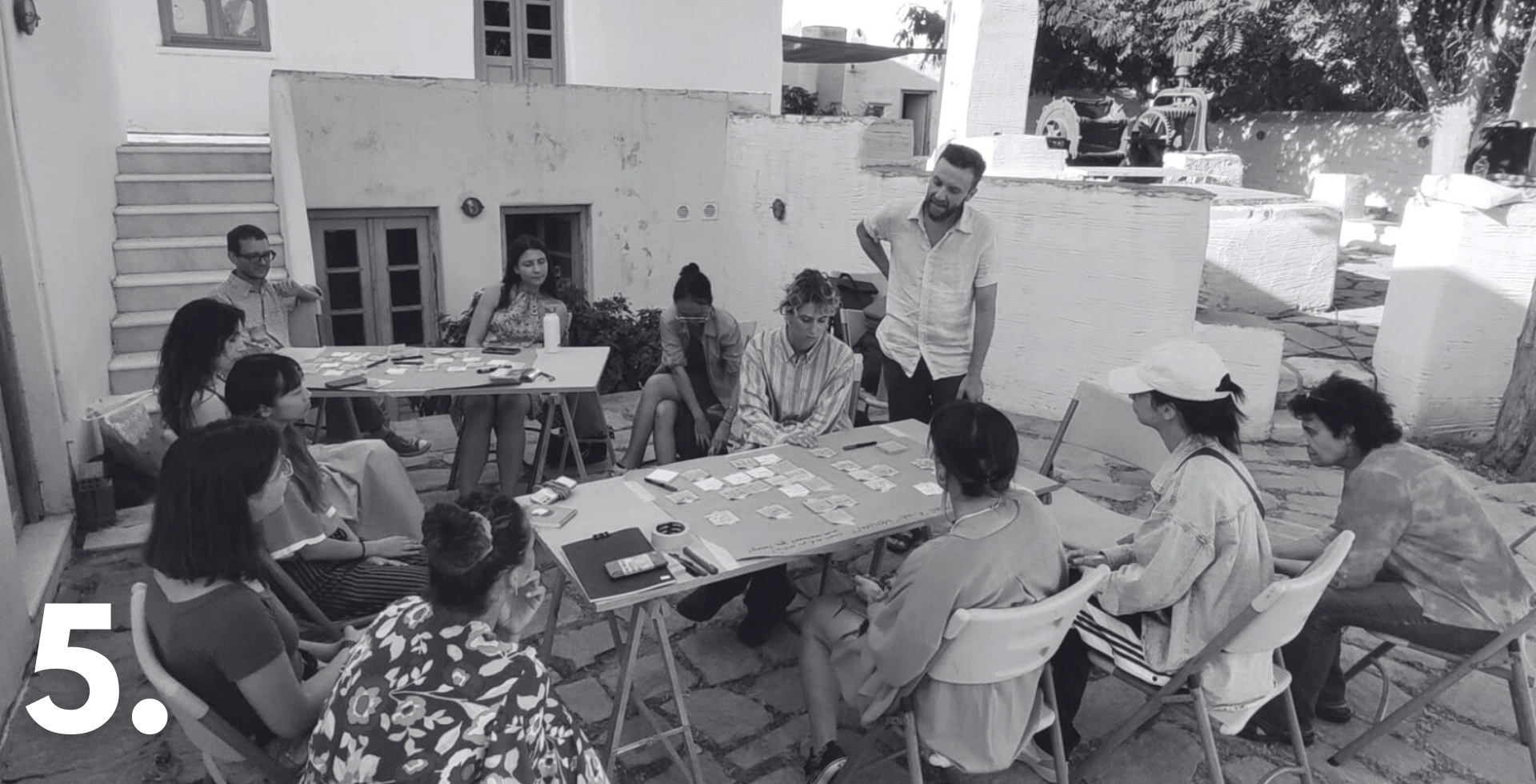
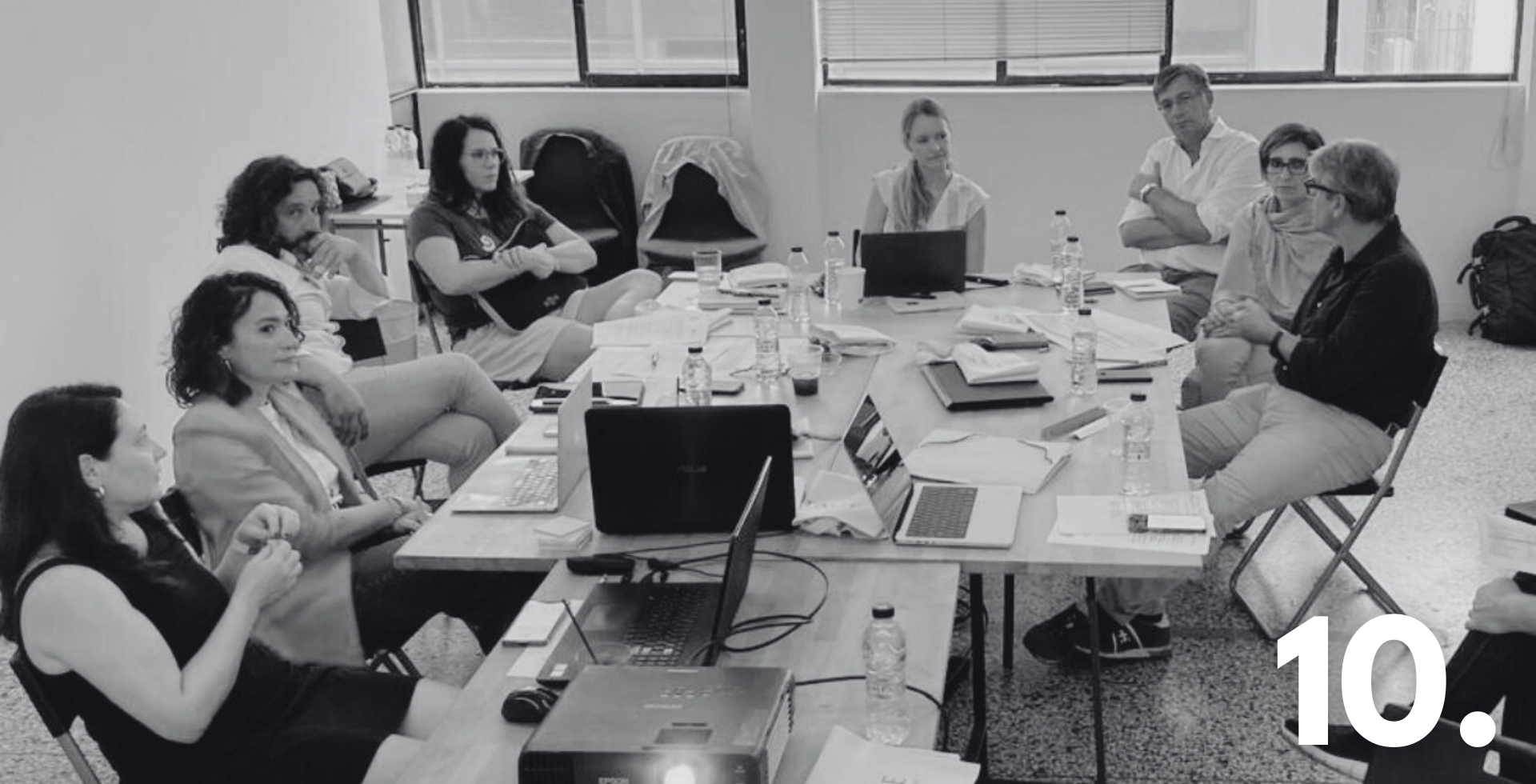
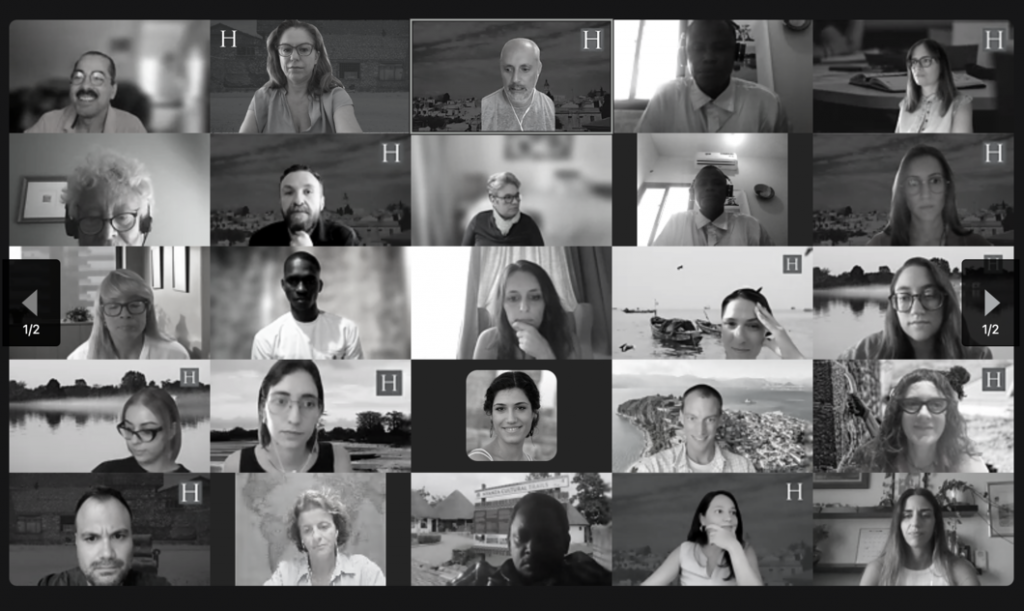
SHIFT Consortium Advances Cultural Heritage Accessibility: Highlights from Athens Event
The HERITΛGE team was very happy to host our colleagues from the SHIFT project Consortium in Athens last week to discuss progress made and the next steps the consortium will take in its work to make cultural heritage more accessible, inclusive and appealing for all. The consortiun also presented the project which is funded by the European Union’s Horizon Europe program, to a select group of heritage professionals, policy makers, and stakeholders on Friday May 24th, during an event at the Athenian Museum.
HERITΛGE’s director, Dr. Evangelos Kyriakidis, opened the event, underlining the significance of the project: “We are very proud of the Organization’s participation in the SHIFT program and happy to be able to present here in Athens the first samples of the partner’s work with the aim of making cultural heritage more accessible, inclusive and attractive,” Kyriakidis said.
Razvan Purcarea from project coordinator SIMAVI briefly presented the project with help from representatives from Queen Mary University of London, the Technical University of Munich, the Foundation for Research and Technology (FORTH), and the technology company audEERING, all members of the SHIFT consortium. During the event, Dr. Angelos Giokas from the Athena Research Center gave a brief presentation of PREMIERE, a project for accessibility and inclusion in the performing arts, which is also funded by the European Union’s Horizon Europe program.
Learn more about SHIFT: https://shift-europe.eu/
Europe’s Common Data Space for Cultural Heritage
By Rob Davies
The European Strategy for data focuses on putting people first in developing technology and defending and promoting European values and rights in the digital world. Data is seen as an essential resource for economic growth, competitiveness, innovation, job creation and societal progress in general. The aim is to create a single market for data that will ensure Europe’s global competitiveness and data sovereignty.
Common European data spaces will be developed and funded in key strategy sectors and areas of public interest, such as health, agriculture or manufacturing. They are intended to ensure that more data becomes available for use in the economy and society, while keeping the companies and individuals who generate the data in control. Data driven applications will benefit citizens and businesses in many ways such as improved health care, safer and cleaner transport systems, lower cost public services, improved sustainability and energy efficiency, more business innovation and by generating new products and services.
The plan is to adopt legislative measures on data governance, access and reuse, e.g. for business-to-government data sharing for the public interest. And to make data more widely available by opening up high value publicly held datasets across the EU and allowing their reuse for free. A big investment in data processing infrastructures, data sharing tools, architectures and governance mechanisms. Thriving data sharing and federated energy-efficient and trustworthy cloud infrastructures and related services.
Among the 14 data spaces initially envisaged, The European Commission has published a recommendation on a common European data space for cultural heritage. The aim is to accelerate the digitisation of cultural heritage assets like cultural heritage monuments and sites, objects and artefacts for future generations, to protect and preserve those at risk, and boost their reuse in domains such as education, sustainable tourism and cultural creative sectors.
Currently cultural tourism represents up to 40% of all tourism in Europe, cultural and creative industries contribute 3.95% of total EU value added (€477 billion) and more than 8 million people are employed within them, through 1.2 million firms – 99.9% of which are SMEs; Member States are encouraged to digitise by 2030 all monuments and sites that are at risk of degradation and half of those highly frequented by tourists. This will contribute to the objectives of the Digital Decade by fostering a secure and sustainable digital infrastructure, digital skills and uptake of technologies by businesses, in particular SMEs.
Europeana, the European digital cultural platform, will be at the basis for building the common data space for cultural heritage by allowing museums, galleries, libraries and archives across Europe to share and reuse the digitised cultural heritage images such as 3D models of historical sites and high quality scans of paintings. Europeana currently offers access to 52 million cultural heritage assets, 45% of which can be reused in various sectors. Images and text make up 97.5% of Europeana’s assets, with only 2.47% audiovisual content and 0.03% in 3D. The collection of 3D assets in particular should see a massive boost, thanks to this latest initiative.
It is envisaged that the common data space for cultural heritage will include a wider variety of data types than the current digital content of Europeana. While these are still to be fully defined, they might be about any aspect of tangible or intangible Cultural Heritage – its creation, description, storage, presentation/performance, transmission, access, preservation, reuse, rights etc.- or possibly even more widely drawn from across the whole spectrum of cultural activity, including data coming from scientific or other fields which eventually constitutes our heritage.
Alongside this, the European collaborative cloud on cultural heritage (ECCCH) is a European Union initiative for a digital infrastructure that will connect cultural heritage institutions and professionals across the EU. It is intended to help protect European cultural heritage while answering to the new requirements of a digitized world. In doing that, it will provide practical benefits to all cultural heritage professionals and museums, developing specific digital collaborative tools for the sector while removing barriers for smaller and remote institutions. The goal is to help cultural heritage institutions, research organisations and other professionals of all sizes and types work with their digital objects in a more visible, interconnected, harmonised, and informed way, allowing them to successfully cope with the challenges the digital transition poses to the sector.
The ECCCH, funded by Horizon Europe, will aim to add a new digital dimension to cultural heritage preservation, conservation, restoration and enhancement by providing cutting-edge technologies for digitising artefacts and researching artworks, paving the way for new transdisciplinary collaboration in the field of cultural heritage, bringing together specialists from a range of disciplines, including scholars, curators, archivists, and conservators.
This ambitious project for a new cutting-edge platform will work in tandem with other European initiatives, such as Europeana and the common European dataspace for cultural heritage, to add a new dimension to the way we approach, conserve and enhance our shared cultural heritage. As part of the ECCCH, two calls for proposals were open until September 2023 to fund. projects which will contribute to setting up the foundations of ECCCH. With an envisaged budget of €110 million until 2025 from Horizon Europe, the ECCCH will be a unique infrastructure that will enable unprecedented transdisciplinary and large-scale collaboration between specialists.
*Rob Davies is HERITΛGE’s Head of European Programs and Chair of the Management Board of the Europeana Network Association (ENA).
*HERITΛGE offers a number of training opportunities on Digital Tools for Cultural Heritage. These include a 3-day workshop, a summer field school, and a credit bearing Certificate in cooperation with HOGENT University.
- 1
- 2