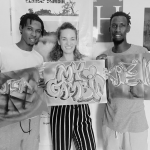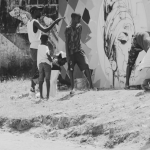Tag Archives: HerMaP Gambia
HERITΛGE Highlights 2024
Training
HERITΛGE celebrated a record-breaking milestone in 2024, training over 1,000 heritage caretakers in a single year. Participants engaged in a wide range of programs, including three-day workshops conducted online and in person, two annual summer schools focusing on digital tools and community engagement, and specialized training tailored to specific regions, topics and organizations. These included programs on Street Art in The Gambia (which also produced a new mural for the country’s National Centre for the Arts and Culture), Heritage interpretation in Rwanda, Project Management for US Heritage Managers, and an introduction to Fundraising and Project Management in Iraq.
Heritage Threatened by Conflict, Natural Disasters, and Climate Change
HERITΛGE continued its mission to protect heritage at risk worldwide, strengthening existing partnerships and forging new ones. In Ukraine, the Digital Museum project that was funded by the Creative Europe’s Culture Helps initiative, trained museum professionals to use digital tools, ensuring operational continuity and community access during wartime. Simultaneously, the two-year Architecture in Times of War: The Ukrainian Model initiative – delivered in cooperation with the Kharkiv School of Architecture and Skeiron and the support of the US Embassy in Kyiv – is equipping students and educators with digital skills to document, preserve, and restore architectural heritage.
In Türkiye, HERITΛGE published comprehensive reports documenting historic sites affected by the February 2023 Türkiye-Syria earthquakes. These reports include protection recommendations and advocate for enhanced cultural heritage recovery in affected provinces. Meanwhile, in Pakistan, a new project launched to safeguard the early Buddhist heritage of the Swat Valley, an area under threat from conflict, climate change, and rapid development. In Yemen, efforts continued to preserve the unique earthen architecture of Shibam, a UNESCO World Heritage Site struggling under the weight of a decade-long civil war.
HERITΛGE in Africa
The HerMaP Africa initiative, generously supported by the Mellon Foundation, has delivered significant impact. Over 75 small heritage projects received funding, alongside the awarding of several fellowships and the training of more than 370 heritage managers in Ethiopia, Ghana, and Rwanda. New partnerships were also established to further these efforts. In The Gambia, HERITΛGE’s ongoing HerMaP Gambia initiative, co-funded by the European Union, provided training to enhance the country’s culture and tourism sectors. The program also facilitated a parliamentary delegation study tour in Greece and partnered with the NCAC to launch the country’s Intangible Cultural Heritage Register, a project supported by UNESCO.
Giving Heritage Managers New Tools
HERITΛGE made strides in empowering heritage managers with innovative tools and practices. The EU-funded SHIFT project advanced its work to make heritage more accessible and inclusive, with a consortium meeting and project presentation held in Athens. The AHEAD initiative, co-funded by the European Union’s Creative Europe program, introduced seminars (now available online) and launched a community-based artistic project in Crete, with similar activities planned for Italy and Spain. HERITΛGE also announced the launch of EMPATHS, a project designed to promote participatory heritage interpretation through new tools and training resources.
Creating Networks, Connecting Professionals
Collaboration and community-building remained central to HERITΛGE’s mission in 2024. The organization continued developing Greece’s Living Heritage Network, supported by the Ministry of Culture, with HERITΛGE actively contributing to its digital and physical infrastructure, member recruitment, and communications. Additionally, the newly established AHEAD Network brings together heritage managers and community members who share a vision of audience engagement and participation.
Knowledge Sharing
HERITΛGE emphasized the importance of knowledge-sharing through active participation in global events and publications. Director Dr. Evangelos Kyriakidis delivered a keynote at the Choc Des Legendes Conference in Ghana, held under the auspices of the country’s First Lady. The organization also sponsored PastForward 2024, the annual conference of the US National Trust for Historic Preservation. Other highlights included workshops and presentations at the 30th Annual Meeting of the European Association of Archaeologists and the ReImagining Public Collections conference in Hungary.
HERITΛGE contributed to a Horizon Europe-funded policy brief on digital cultural heritage and shared expertise through webinars, seminars, and public lectures. Notable online resources include audience development webinars from the AHEAD initiative and webinars on architectural preservation in Ukraine.
1st Global Staff Summit
Reflecting the growth in HERITΛGE’s activities and team, the organization hosted its inaugural Global Staff Summit in September. This online event brought together staff working in Africa, Asia, Europe and the Americas , marking the beginning of an annual tradition to foster collaboration and alignment across our expanding network.
Intangible Cultural Heritage Register Launched
 The Gambia’s National Centre for Arts and Culture (NCAC) and the Heritage Management Organization (HERITΛGE) proudly launched The Gambia’s Intangible Cultural Heritage Register on December 16th, a project realized under the auspices of the country’s Ministry of Tourism, Arts, and Culture.
The Gambia’s National Centre for Arts and Culture (NCAC) and the Heritage Management Organization (HERITΛGE) proudly launched The Gambia’s Intangible Cultural Heritage Register on December 16th, a project realized under the auspices of the country’s Ministry of Tourism, Arts, and Culture.
The Register documents elements of The Gambia’s intangible cultural heritage (ICH) selected during the Pilot Innvetory Project on the contribution of ICH to sustainable development in the country, along with the role of this heritage in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) as established by the field findings of research conducted in 2021. Both activities were funded by UNESCO.
“This Register is a great step forward in our desire to conserve, preserve and interpret
Gambian culture,” said Hassoum Ceesay, Director General of the NCAC. “The Register lists 30 elements of our ICH including the domain, description, bearer Community and pictures and videos to illustrate the element.”
Ceesay added that following the pilot inventory, the NCAC has received extra funding to widen the inventory exercise to all Regions of The Gambia.
HERIΤΛGE will be hosting the inventory on its digital infrastructure and working to enrich and disseminate the information in the framework of its HerMaP Gambia program, an initiative co-funded by the European Union to upskill and strengthen the country’s heritage and tourism sectors.
The Gambia: Community Tourism Planning & Development
From the 11th to 15th November 17 heritage professionals joined HERITAGE’s Community Tourism Planning & Development workshop that was organized in the framework of HerMaP Gambia, an initiative co-funded by the European Union that aims to enrich the understanding and appreciation of Gambian cultural heritage while enhancing the capacity of key stakeholders in the cultural and tourism sectors.
Tim Healing led the online course which was aimed at helping heritage professionals build the knowledge and skills necessary to develop sustainable community tourism projects. Through these projects, key stakeholders from the Gambia Tourist Board, Institute for Travel and Tourism of The Gambia, Juffureh Heritage Village Museum, Senegambia Stone Circle Tour Guide Association, JJB Kankurang Festival Committee as well as Independent participants, were encouraged to also address issues such as how to promote cultural preservation, economic empowerment, and environmental sustainability.
Participants worked on case studies from projects including Lamu in Kenya, Raqchi in Peru, Tourism Development in the Mursi Community of Ethiopia, The Green Valley Community Tourism Project, Managing Tourist Impact on the Cultural Events of the Maasai Mara Community, The Phong Nha-Ke Bang National Park, and the Community-Based Tourism Initiative in Vietnam.
By focusing on community resource mobilisation, partnership building, financial literacy, and effective branding, the workshop aimed to equip participants with the knowledge and skills to create authentic tourism experiences that support local development while increasing awareness of cultural heritage management . Participation with the workshop was lively with attendees demonstrating significant interest in the subject. Despite being online, the workshop was also highly interactive, combining discussions, presentations, and group exercises which fostered an engaging learning environment. The collaborative activities encouraged the sharing of ideas and best practices, ensuring the content resonated with participants and was applicable to their local contexts.
“The workshop benefited greatly from the participants’ hands-on experience in community tourism, which added depth to the discussions and activities. Their practical knowledge allowed for a more insightful and relevant exchange of ideas, making the sessions both engaging and meaningful. I’m eager to see how they apply the strategies and concepts learned to further develop tourism projects,” said Mina Morou – HerMaP Gambia Project Manager.
*Tim Healing is our interim director of African Grants and capacity development officer, helping small heritage organizations in Africa develop an application and ensure they manage their grant efficiently. Tim has over thirty years’ experience working as a project manager and has a professional background in project management, community and NGO development.
A Street Art Workshop in The Gambia
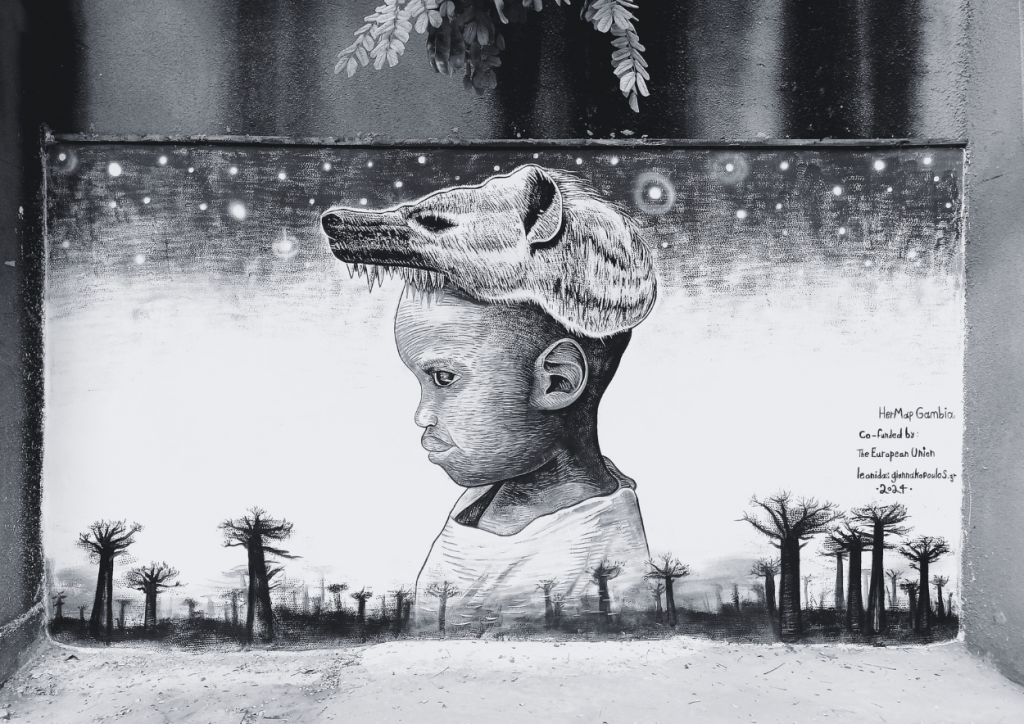

Mural by Leonidas Giannakopoulos, created for the NCAC premises in Banjul, in the framework of HerMaP Gambia, an initiative co-funded by the EU.
From 23rd October to 1st November, HERITΛGE held a Street Art Workshop in the Gambia. Street art serves as a vibrant and dynamic medium to bring history, culture, and identity to life and the workshop aimed to emphasize the power of creative expression in preserving and showcasing cultural heritage. The workshop was led by Leonidas Giannakopoulos*, a Greek artist whose murals adorn a number of central buildings in Greece and beyond. Giannakopoulos also created a mural for the premises of The Gambia’s National Centre for the Arts and Culture (NCAC) during the workshop.
The training is part of HerMaP Gambia, an initiative co-funded by the EU that aims to enrich the understanding and appreciation of Gambian cultural heritage while enhancing the capacity of key stakeholders in the cultural sector. HERITΛGE has been working with the street artists of Galloya, a creative team of young locals that has also put together a local festival, for the past two years in the framework of HerMaP Gambia.
Nine participants from around The Gambia joined the ten-day workshop where they delved into the history, significance, and key movements of graffiti and street art. Through this initiative, the program highlighted the importance of art as both a cultural tool and a means of celebrating and preserving heritage in a living, evolving form.
The workshop explored how cultural heritage can be commemorated through artistic representation, ensuring that elements of heritage resonate with the present generation. They also focused on practicing essential techniques like stencilling and design principles. On the third day, they focused on personal production, allowing each participant to create their own unique artwork.
“I really enjoyed the big thirst for knowledge all our participants had and I hope everything I showed them and taught them was inspiring. I believe they will use all this knowledge because I saw a big thirst for artistic expression. In their next works I believe they will apply all the things that they learned and they will keep on learning!” said trainer Leonidas Giannakopoulos.
Participants were enthusiastic and fully engaged, producing creative and thought-provoking street art reflecting local culture. “The knowledge and skills we gained during this experience have been truly invaluable” said Amadou Mousa, a street artist from Galloya and one of the founders of the local festival. “Leonidas’ guidance has not only enhanced our artistic abilities but also inspired us to explore new ways of expressing creativity within our community,” he added.
Following this intensive workshop, an additional five days were devoted to the creation of a public artwork at the NCAC premises. During this time, participants observed advanced techniques and engaged closely with the detailed process of producing impactful public art. They gained hands-on experience in conceptualization, production, and project management, enhancing their appreciation for the commitment and precision behind large-scale street art projects.
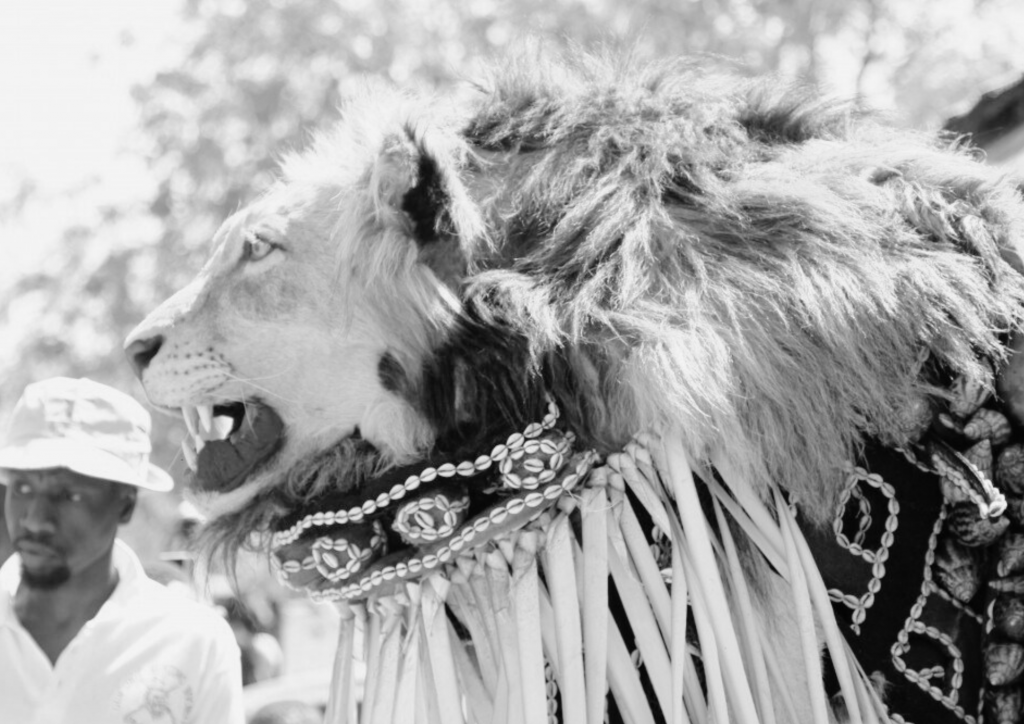
“I wanted to create an artwork that refers to the people here in The Gambia, to the country’s young people that bring the future,” said Giannakopoulos. “So I wanted to paint the portrait of a young child from the area of Banjul and express the culture of this country by painting him with a mask of a hyena over a landscape of baobab trees, a very powerful tree that gives so many things to the people, it is not only about food or drink but is also spiritual.”
*Leonidas Giannakopoulos studied painting and printmaking at the School of Ffine Arts of Athens, and has since been commissioned to paint several murals for municipalities, festivals, public buildings and private companies around the world.
**Photos by Leonidas Giannakopoulos, Nefeli Papanagiotou, and the HerMaP Gambia team and beneficiaries in The Gambia
Festival Management Training in The Gambia
Over 16th and 17th of October, 27 participants from 10 institutions across Gambia joined us for the Festival Management and Operations Training. The two-day course aimed at enhancing participants’ understanding of essential concepts and practices to create impactful, well-organized, and environmentally conscious festivals that engage and benefit their communities.
It was led by Hanine-K Lakkis, a cultural specialist, events director, and trainer, and Mina Morou, The Gambia Programmes Manager for HERITΛGE.
The training is part of HerMap Gambia, an initiative co-funded by the EU that aims to enrich the understanding and appreciation of Gambian cultural heritage while enhancing the capacity of key stakeholders in the cultural sector. It was developed in direct response to requests from five distinct festival organizing groups seeking our expertise to enhance their event planning and management skills. Recognizing the unique challenges and opportunities within festival management, HERITΛGE designed this program to equip participants with essential skills in festival planning, marketing, operations, safety, and sustainability.
By addressing these core areas, HERITΛGE aims to strengthen the capacity of local actors to create impactful, well-organized, and environmentally conscious festivals that engage and benefit their communities. This tailored approach ensures that participants can meet both their organizational goals and the growing expectations of their audiences.
On the first day, participants from Kankurang, Wassu Stone Circles, Niumi Fort Bullen, Roots, Galloya Street Art Festivals as well as Kubuneh and Galloya Cultural Festivals and National Centre for the Arts and Culture (NCAC), Gambia Tourist Board, the Gambia Youth Chamber of Commerce and independent organizers were instructed in the fundamentals of festivals, including their types, purposes, and impacts, along with detailed guidance on planning aspects such as venue selection, programming, and marketing strategies. On the second, they went over operational considerations, such as risk and crowd management, and sustainable practices to minimize environmental impact.
“I want, on behalf of the National Centre for Arts and Culture, to express our sincere appreciation to the Heritage Management Organization and all the Facilitators for offering this valuable training opportunity to our festival organizers,” said Sanna B. Jarju, Head of the Department for Literature, Performing and Fine Arts of the NCAC.
“The training is done at a time when there are a large number of emerging community-based festivals, most of whom strive for sustainability…Festivals are an important way to safeguard our cultural heritage and enable the attainment of the UN Sustainable Development Goals in The Gambia,” he added.
HERITΛGE in the News
Our teams are working around the world to fulfill the HERITΛGE mission. Here is how some of our work has been featured in the press in the last few months.
Heritage Threatened by Conflict
HERITΛGE has launched a new project to safeguard Ukraine’s cultural heritage. Architectural Heritage Preservation in Times of War: The Ukrainian Model is being realized in cooperation with the Kharkiv School of Architecture and Skeiron, with generous support from the U.S. Embassy’s Public Diplomacy Section in Ukraine. The project has been featured in the latest issue of Popular Archaeology as well as in Ukrainian media.
HerMaP Gambia
The Gambia’s National Assembly’s Committee for Culture and Tourism recently embarked on a Parliamentary Study Tour in Thessaloniki. This visit, conducted as part of the HerMaP Gambia program co-funded by the European Union, was widely covered in the Gambian media, including prominent news programs and The Voice newspaper.
Watch the QTV bulletin (start at 14:18) or read the article in The Voice.
HERITΛGE also delivered workshops in The Gambia on various aspects of cultural management, including Festival Management, which was covered by The Voice.
African Heritage Grants
HERITΛGE’s small grants for African heritage initiative, supported by the Mellon Foundation, recently funded Restoring Ilukwe House, a project by the NGO Legacy to restore a historic building in Lagos’ railway compound. Coverage of this initiative appeared in Nigeria’s The Guardian.
The Republic, a Nigeria-based magazine and platform of socio-economic and political commentary, criticism and cultural discourse, has received a substantial grant from the Mellon Foundation to support its mission to establish itself as a regional, leading hub/platform for Black and Africa-focused ideas and critical perspectives; and to further connect Africa and the African diaspora on critical issues, with the help of HERITΛGE.
Greek Living Heritage Network
As a founding member of the Living Heritage Network in Greece, HERITΛGE continues to support and celebrate Greece’s living heritage. Theodosia Maroutsi recently discussed the Network on NaMaste, a cultural program on Greece’s national broadcaster ERA2.
Greek speakers can listen to the show here.